China is a large country with a long history. And it is one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world. Usually when people think of “Chinese”, it is Mandarin that they are picturing. Mandarin or you can called it “Putonghua” is official language of China.
In fact, there are eight major dialects in China and hundreds of less common ones.

1.Modern Standard Mandarin.
It is based on the original Beijing dialect of Mandarin, The user population accounts is more than 70 % of the total number of the Han people.
2.Yue(Cantonese)
Yue(Cantonese) dialect is represented by Guangzhou dialect. Most Yue speakers in mainland China can be found in Guangdong province. Cantonese is the official as well as the dominant language in Macau and Hong Kong.Also it is the fourth spoken language in Australia and the second most spoken language in New Zealand.The user population is about 10% of the total number of Han people.Cantonese is spoken by nearly 120 million people around the world.
3.Wu
Wu dialect is represented by Suzhou dialect and Shanghai dialect.People who speak Wu dialect are mainly distributed in the eastern part of China,with a population of more than 90 million.The user population is about 8.4% of the total Han people.
4.Xiang
Xiang dialect is represented by Changsha dialect. Distributed in most parts of Hunan Province. The user population is about 5% of the total number of Han people.
5.Hakka
Hakka dialect is represented by Meizhou dialect. It mainly distributed in the east, south and north of Guangdong province, southeast of guangxi province, west of fujian province .The user population is about 4% of the total Han people.
6.Min(Fujian dialect&South Fujian dialect)
Most Min speakers are lives in the Fujian province, as well as Taiwan. The user population is about 1.2% of the total Han people.
7.Gan
Gan dialect is represented by Nanchang dialect. Jiangxi province is the main centre for speakers of Gan. The user population is about 2.4% of the total population of the Han people.
Why Mandarin & Cantonese Are Important Languages in China
Mandarin
Mandarin, also known as Putonghua , is the most-spoken language in the world, with over 1.5 billion speakers. It has been the official language of China since 1913 and all schools in China are supposed to teach in Mandarin. A person who wants to be a teacher has to pass the Mandarin level test. Thus, it can be heard across the country. Some elderly people in rural areas will also speak at least a little Mandarin. Even if it is only some basics with a strong accent.

Cantonese
Cantonese is the second most spoken Chinese language. It is not only spoken in Guangdong province or in Macau and Hong Kong but also widely used in several countries in Southeast Asia( Such as Singapore, Malaysia)and in the west.( New York Chinatown, San Francisco, Los Angeles, Paris and other overseas Chinese communities). The language is spoken by around 80 million people. Also Guangzhou is a port city located in the Pearl River Delta, which is in China’s southeastern part. Guangzhou is a important center of culture since long time ago. Thus Cantonese became a common and prestige dialect and quickly spread into the surrounding areas.
If you are a business owners and want to expand into Southeast China and Southeast Asia, you need to learn Cantonese so you will have an opportunity to access to several businesses in these areas.
The difference between Mandarin & Cantonese
Mandarin and Cantonese are very different in both their written and spoken forms. Especially in the grammar and pronunciation. There are also differences in sentence structure, especially in verb placements.
1.Number of tones: There are 4 basic tones in Mandarin. Cantonese is often said to have 9 tones.
2.Basic word: A word may have a completely different meaning in Mandarin and Cantonese .
3.Initial consonants: Cantonese has far fewer initial consonants than Mandarin.
4.Vowel length: Cantonese has a much longer vowel length. The pronounce of Cantonese is much closer to the ancient Chinese.
Useful phrase in Mandarin & Cantonese
1.你好( nǐ hǎo)
Meaning: Hello
In Chinese
In Cantonese
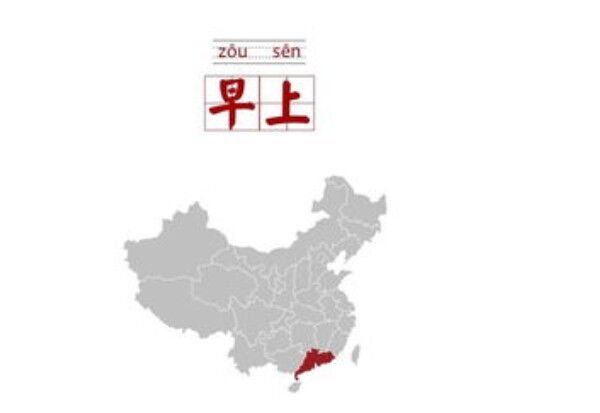
2.早上好( zǎo shàng hǎo)
Meaning: Good Morning
In Chinese
In Cantonese
3.谢谢 ( xiè xiè )
Meaning: Thank you
In Chinese
In Cantonese
4.对不起( duì bù qǐ)
Meaning: Sorry
In Chinese
In Cantonese
5.再见( zài jiàn )
Meaning:Goodbye
In Chinese
In Cantonese
6.回家 (huí jiā)
Meaning: Go home
In Chinese
In Cantonese
7.我喜欢你( wǒ xǐ huān nǐ)
Meaning: I like you
In Chinese
In Cantonese
Further reading:
5 Differences between Chinese and English
How to Say Thank You in Chinese
Baggage Rules of China Railway





